python调用SCIP求解TSP(callback方式实现消除子环路subtour)_scip 无可行解 返回-程序员宅基地
1 TSP数学模型
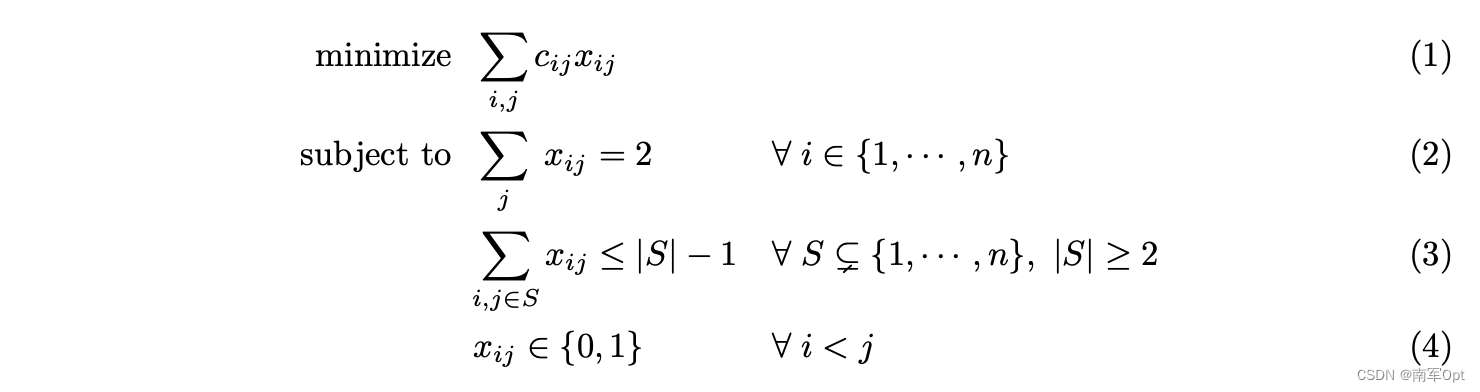
2 callback消除子环路(subtour)
- callback解决方案
The constraints (3) exclude subtours by imposing that for any proper subset S of the vertex set V such that |S| ≥ 2 a solution cannot encompass a cycle within S. However, as there is an exponential number of subsets of V , it is impractical to specify all of these constraints. A possible approach is to iteratively solve the problem, starting without these constraints and after each solving round add constraints (3) violated by the current solution.
- SCIP中的callback方式
一般商业求解器Gurobi或者CPLEX中直接提供的callback(回调函数)的方法,SCIP采用的是constraint handler的方式,使用起来没那么方便,需要自定义一个继承了约束处理的类Conshdlr,覆写conscheck、consenfolp、conslock方法。看源码其实就是callback的一种实现形式而已,其运行日志显示也是迭代运行求解的。
3 python调用SCIP求解TSP
- 完整python代码如下:
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import itertools
from pyscipopt import Model, Conshdlr, quicksum, SCIP_RESULT
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 替换sans-serif字体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正常显示负号
# 继承约束处理的类
class TSPconshdlr(Conshdlr):
def __init__(self, variables):
self.variables = variables
def find_subtours(self, solution = None):
# find subtours in the graph induced by the edges {i,j} for which x[i,j] is positive
# at the given solution; when solution is None, then the LP solution is used
# 获取所有连接边
edges = []
x = self.variables
for (i, j) in x:
if self.model.getSolVal(solution, x[i, j]) > 1.e-6:
edges.append((i, j))
# 判断图是否有连接,如果返回的长度=1,则说明没有子连接
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_edges_from(edges)
components = list(nx.connected_components(G))
if len(components) == 1:
return []
else:
return components
# checks whether solution is feasible, ie, if there are no subtours;
# since the checkpriority is < 0, we are only called if the integrality
# constraint handler didn't find infeasibility, so solution is integral
def conscheck(self, constraints, solution, check_integrality,
check_lp_rows, print_reason, completely, **results):
""" calls feasibility check method of constraint handler """
if self.find_subtours(solution):
return {
"result": SCIP_RESULT.INFEASIBLE}
else:
return {
"result": SCIP_RESULT.FEASIBLE}
def consenfolp(self, constraints, n_useful_conss, sol_infeasible):
""" calls enforcing method of constraint handler for LP solution for all constraints added """
subtours = self.find_subtours()
if subtours:
x = self.variables
# 添加子环消除路约束
for subset in subtours:
self.model.addCons(quicksum(x[i, j] for(i, j) in pairs(sorted(subset))) <= len(subset) - 1)
print("cut: len(%s) <= %s" % (subset, len(subset) - 1))
return {
"result": SCIP_RESULT.CONSADDED}
else:
return {
"result": SCIP_RESULT.FEASIBLE}
def conslock(self, constraint, locktype, nlockspos, nlocksneg):
# 可以直接跳过
pass
# def conslock(self, constraint, locktype, nlockspos, nlocksneg):
# x = self.variables
# for (i,j) in x:
# self.model.addVarLocks(x[i,j], nlocksneg, nlockspos)
def pairs(nodes):
return itertools.combinations(nodes, 2)
def get_route_data(edges):
# 解析获取路径,构成一个环
routes = []
for i in range(len(edges)):
if i == 0:
routes.append(edges[0])
edges.pop(0)
else:
pre = routes[-1]
connected_node = pre[1]
for j in range(len(edges)):
aft = edges[j]
if connected_node in aft:
if aft[0] == connected_node:
chosen_node = (aft[0], aft[1])
elif aft[1] == connected_node:
chosen_node = (aft[1], aft[0])
routes.append(chosen_node)
edges.pop(j)
break
i = i+1
return routes
def plot_pic(route, city_location):
plt.figure()
# 绘制散点
x = np.array(city_location)[:, 0] # 横坐标
y = np.array(city_location)[:, 1] # 纵坐标
plt.scatter(x, y, color='r')
# 绘制城市编号
for i, txt in enumerate(range(1, len(city_location) + 1)):
plt.annotate(txt, (x[i], y[i]))
# 绘制方向
x0 = x[route]
y0 = y[route]
for i in range(len(city_location) - 1):
plt.quiver(x0[i], y0[i], x0[i + 1] - x0[i], y0[i + 1] - y0[i], color='b', width=0.005, angles='xy', scale=1,
scale_units='xy')
plt.quiver(x0[-1], y0[-1], x0[0] - x0[-1], y0[0] - y0[-1], color='b', width=0.005, angles='xy', scale=1,
scale_units='xy')
plt.title('TSP')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.savefig('./TSP.png')
plt.show()
def pre_test_data():
# 城市节点的位置信息,一行代表一个城市的横坐标及纵坐标
city_location = [[ 94, 99],
[ 66, 67],
[ 14, 78],
[ 95, 56],
[ 68, 9],
[ 26, 20],
[ 51, 67],
[ 39, 39],
[ 5, 55],
[ 12, 33],
[ 55, 85],
[ 98, 46],
[ 36, 39],
[ 65, 100],
[ 57, 89],
[ 88, 24],
[ 53, 96],
[ 91, 41],
[ 32, 69],
[ 38, 38],
[ 38, 39],
[ 85, 100],
[ 7, 37],
[ 85, 96],
[ 89, 48],
[ 85, 35],
[ 32, 29],
[ 31, 25],
[ 20, 17],
[ 75, 21],
[ 74, 29],
[ 6, 32],
[ 20, 81],
[ 62, 1],
[ 11, 48],
[ 1, 69],
[ 99, 70],
[ 20, 27],
[ 25, 42],
[ 6, 31],
[ 78, 24],
[ 42, 39],
[ 83, 30],
[ 94, 10],
[ 90, 37],
[ 76, 73],
[ 9, 56],
[ 39, 33],
[ 74, 15],
[ 77, 14]]
nodes = list(range(len(city_location))) # 节点集合
# 计算距离成本矩阵 distance, 直接使用欧式距离
distance = {
}
for (i, j) in pairs(nodes):
distance[(i, j)] = ((city_location[i][0]-city_location[j][0])**2+(city_location[i][1]-city_location[j][1])**2)**0.5
return nodes, city_location, distance
def solve_tsp(nodes, distance):
# 构建模型
model = Model("TSP")
# 定义变量: 为了减少决策变量,节点i和j是否连接(无方向),即(1,2)代表1和2连接,不代表1->2
x = {
}
for (i, j) in pairs(nodes):
x[i, j] = model.addVar(vtype="B", name="x(%s,%s)" % (i, j))
# 添加流约束
for i in nodes:
model.addCons(quicksum(x[j, i] for j in nodes if j < i) +
quicksum(x[i, j] for j in nodes if j > i) == 2, "Degree(%s)" % i)
# 去除子环路
conshdlr = TSPconshdlr(x)
model.includeConshdlr(conshdlr, "TSP", "TSP subtour eliminator", chckpriority=-10, needscons=False)
model.setBoolParam("misc/allowstrongdualreds", False)
# 设置目标
model.setObjective(quicksum(distance[i, j] * x[i, j] for (i, j) in pairs(nodes)), "minimize")
# 求解
model.hideOutput()
model.optimize()
# 获取结果
if model.getStatus() != 'infeasible':
edges = []
for (i, j) in x:
if model.getVal(x[i, j]) > 1.e-6:
edges.append((i, j))
routes = get_route_data(edges)
print("Optimal routes:", routes)
print("Optimal cost:", model.getObjVal())
else:
print('model is infeasible')
return routes
if __name__ == "__main__":
############## 准备测试数据 ##############
nodes, city_location, distance = pre_test_data()
############## 建模 & 求解 ##############
route = solve_tsp(nodes, distance)
############## 绘图结果 ##############
plot_pic(route, city_location)
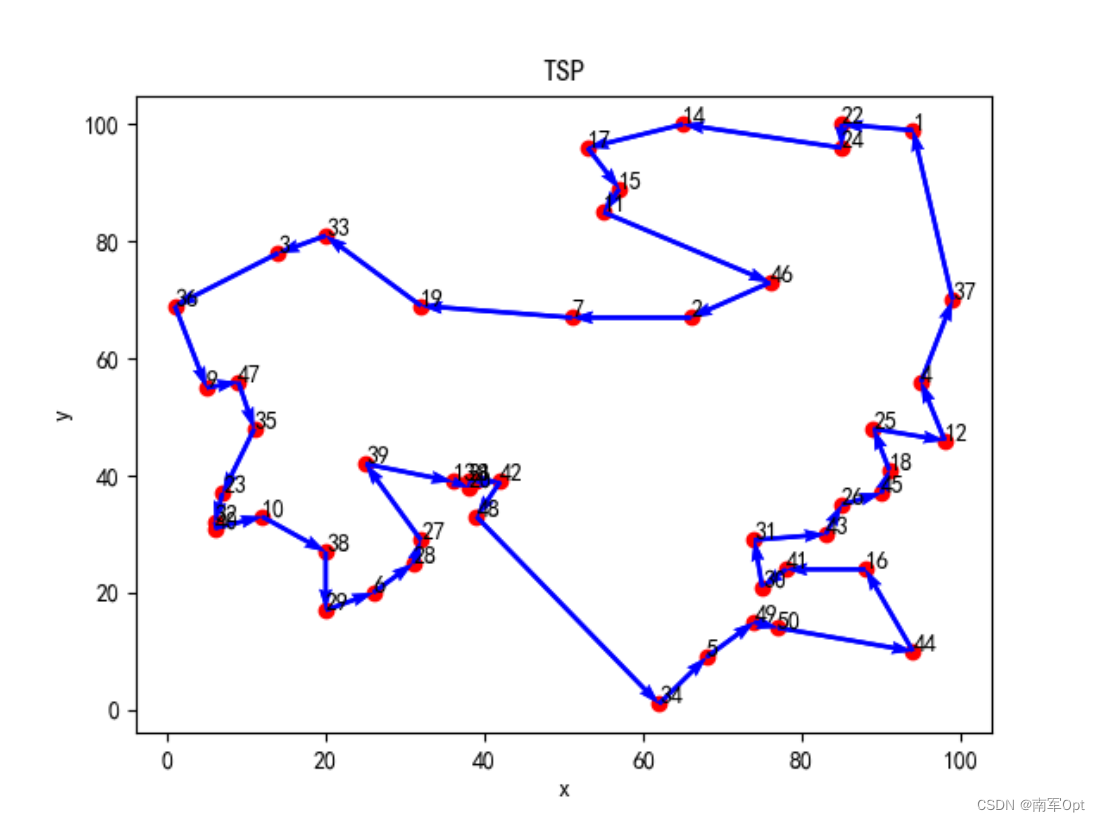
4 求解结果
4.1 log日志
cut: len({
0, 21, 23}) <= 2
cut: len({
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 24, 25, 26, 27, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 38, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49}) <= 32
cut: len({
37, 28, 5}) <= 2
cut: len({
9, 31, 22, 39}) <= 3
cut: len({
16, 10, 13, 14}) <= 3
cut: len({
40, 29, 30}) <= 2
cut: len({
0, 1, 36, 6, 10, 45, 13, 14, 16, 21, 23}) <= 10
cut: len({
32, 2, 18}) <= 2
cut: len({
24, 11, 3}) <= 2
cut: len({
48, 33, 4}) <= 2
cut: len({
34, 37, 5, 39, 7, 9, 41, 38, 12, 47, 19, 20, 22, 26, 27, 28, 31}) <= 16
cut: len({
8, 35, 46}) <= 2
cut: len({
40, 42, 43, 15, 49, 29, 30}) <= 6
cut: len({
17, 44, 25}) <= 2
cut: len({
0, 13, 21, 23}) <= 3
cut: len({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 15, 17, 18, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49}) <= 34
cut: len({
7, 41, 12, 19, 20}) <= 4
cut: len({
16, 10, 14}) <= 2
cut: len({
31, 22, 39}) <= 2
cut: len({
0, 1, 36, 6, 10, 45, 13, 14, 16, 18, 21, 23}) <= 11
cut: len({
32, 2, 35}) <= 2
cut: len({
24, 11, 3, 17}) <= 3
cut: len({
33, 4, 40, 42, 43, 44, 15, 48, 49, 25, 29, 30}) <= 11
cut: len({
37, 5, 39, 7, 9, 41, 38, 12, 47, 19, 20, 22, 26, 27, 28, 31}) <= 15
cut: len({
8, 34, 46}) <= 2
cut: len({
0, 10, 13, 14, 16, 21, 23}) <= 6
cut: len({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49}) <= 42
cut: len({
0, 1, 36, 10, 45, 13, 14, 16, 21, 23}) <= 9
cut: len({
2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 18, 19, 20, 22, 26, 27, 28, 31, 32, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41, 46, 47}) <= 23
cut: len({
3, 11, 44, 17, 24}) <= 4
cut: len({
33, 4, 40, 42, 43, 15, 48, 49, 25, 29, 30}) <= 10
cut: len({
0, 1, 6, 10, 13, 45, 14, 16, 21, 23}) <= 9
cut: len({
2, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12, 18, 19, 20, 22, 26, 27, 28, 31, 32, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41, 46, 47}) <= 22
cut: len({
11, 3, 36}) <= 2
cut: len({
33, 4, 40, 42, 43, 15, 48, 49, 29, 30}) <= 9
cut: len({
24, 17, 44, 25}) <= 3
Optimal routes: [(0, 21), (21, 23), (23, 13), (13, 16), (16, 14), (14, 10), (10, 45), (45, 1), (1, 6), (6, 18), (18, 32), (32, 2), (2, 35), (35, 8), (8, 46), (46, 34), (34, 22), (22, 31), (31, 39), (39, 9), (9, 37), (37, 28), (28, 5), (5, 27), (27, 26), (26, 38), (38, 12), (12, 19), (19, 20), (20, 7), (7, 41), (41, 47), (47, 33), (33, 4), (4, 48), (48, 49), (49, 43), (43, 15), (15, 40), (40, 29), (29, 30), (30, 42), (42, 25), (25, 44), (44, 17), (17, 24), (24, 11), (11, 3), (3, 36), (36, 0)]
Optimal cost: 508.0830635384923
4.2 绘图结果
智能推荐
2022黑龙江最新建筑八大员(材料员)模拟考试试题及答案_料账的试题-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读529次。百分百题库提供建筑八大员(材料员)考试试题、建筑八大员(材料员)考试预测题、建筑八大员(材料员)考试真题、建筑八大员(材料员)证考试题库等,提供在线做题刷题,在线模拟考试,助你考试轻松过关。310项目经理部应编制机械设备使用计划并报()审批。A监理单位B企业C建设单位D租赁单位答案:B311对技术开发、新技术和新工艺应用等情况进行的分析和评价属于()。A人力资源管理考核B材料管理考核C机械设备管理考核D技术管理考核答案:D312建筑垃圾和渣土._料账的试题
chatgpt赋能python:Python自动打开浏览器的技巧-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读614次。本文由chatgpt生成,文章没有在chatgpt生成的基础上进行任何的修改。以上只是chatgpt能力的冰山一角。作为通用的Aigc大模型,只是展现它原本的实力。对于颠覆工作方式的ChatGPT,应该选择拥抱而不是抗拒,未来属于“会用”AI的人。AI职场汇报智能办公文案写作效率提升教程 专注于AI+职场+办公方向。下图是课程的整体大纲下图是AI职场汇报智能办公文案写作效率提升教程中用到的ai工具。_python自动打开浏览器
Linux中安装JDK-RPM_linux 安装jdk rpm-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读545次。Linux中安装JDK-RPM方式_linux 安装jdk rpm
net高校志愿者管理系统-73371,计算机毕业设计(上万套实战教程,赠送源码)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读25次。免费领取项目源码,请关注赞收藏并私信博主,谢谢-高校志愿者管理系统主要功能模块包括页、个人资料(个人信息。修改密码)、公共管理(轮播图、系统公告)、用户管理(管理员、志愿用户)、信息管理(志愿资讯、资讯分类)、活动分类、志愿活动、报名信息、活动心得、留言反馈,采取面对对象的开发模式进行软件的开发和硬体的架设,能很好的满足实际使用的需求,完善了对应的软体架设以及程序编码的工作,采取SQL Server 作为后台数据的主要存储单元,采用Asp.Net技术进行业务系统的编码及其开发,实现了本系统的全部功能。
小米宣布用鸿蒙了吗,小米OV对于是否采用鸿蒙保持沉默,原因是中国制造需要它们...-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读122次。原标题:小米OV对于是否采用鸿蒙保持沉默,原因是中国制造需要它们目前华为已开始对鸿蒙系统大规模宣传,不过中国手机四强中的另外三家小米、OPPO、vivo对于是否采用鸿蒙系统保持沉默,甚至OPPO还因此而闹出了一些风波,对此柏铭科技认为这是因为中国制造当下需要小米OV几家继续将手机出口至海外市场。 2020年中国制造支持中国经济渡过了艰难的一年,这一年中国进出口贸易额保持稳步增长的势头,成为全球唯一..._小米宣布用鸿蒙系统
Kafka Eagle_kafka eagle git-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.3k次。1.Kafka Eagle实现kafka消息监控的代码细节是什么?2.Kafka owner的组成规则是什么?3.怎样使用SQL进行kafka数据预览?4.Kafka Eagle是否支持多集群监控?1.概述在《Kafka 消息监控 - Kafka Eagle》一文中,简单的介绍了 Kafka Eagle这款监控工具的作用,截图预览,以及使用详情。今天_kafka eagle git
随便推点
Eva.js是什么(互动小游戏开发)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1k次,点赞29次,收藏19次。Eva.js 是一个专注于开发互动游戏项目的前端游戏引擎。:Eva.js 提供开箱即用的游戏组件供开发人员立即使用。是的,它简单而优雅!:Eva.js 由高效的运行时和渲染管道 (Pixi.JS) 提供支持,这使得释放设备的全部潜力成为可能。:得益于 ECS(实体-组件-系统)架构,你可以通过高度可定制的 API 扩展您的需求。唯一的限制是你的想象力!_eva.js
OC学习笔记-Objective-C概述和特点_objective-c特点及应用领域-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。Objective-C概述Objective-C是一种面向对象的计算机语言,1980年代初布莱德.考斯特在其公司Stepstone发明Objective-C,该语言是基于SmallTalk-80。1988年NeXT公司发布了OC,他的开发环境和类库叫NEXTSTEP, 1994年NExt与Sun公司发布了标准的NEXTSTEP系统,取名openStep。1996_objective-c特点及应用领域
STM32学习笔记6:TIM基本介绍_stm32 tim寄存器详解-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读955次,点赞20次,收藏16次。TIM(Timer)定时器定时器可以对输入的时钟进行计数,并在计数值达到设定值时触发中断16位计数器、预分频器、自动重装寄存器的时基单元,在 72MHz 计数时钟下可以实现最大 59.65s 的定时,59.65s65536×65536×172MHz59.65s65536×65536×721MHz不仅具备基本的定时中断功能,而且还包含内外时钟源选择、输入捕获、输出比较、编码器接口、主从触发模式等多种功能。_stm32 tim寄存器详解
前端基础语言HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 学习指南_艾编程学习资料-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.5k次。对于任何有兴趣学习前端 Web 开发的人来说,了解 HTML、CSS 和JavaScript 之间的区别至关重要。这三种前端语言都是您访问过的每个网站的用户界面构建块。而且,虽然每种语言都有不同的功能重点,但它们都可以共同创建令人兴奋的交互式网站,让用户保持参与。因此,您会发现学习所有三种语言都很重要。如果您有兴趣从事前端开发工作,可以通过多种方式学习这些语言——在艾编程就可以参与到学习当中来。在本文中,我们将回顾每种语言的特征、它们如何协同工作以及您可以在哪里学习它们。HTML vs C._艾编程学习资料
三维重构(10):PCL点云配准_局部点云与全局点云配准-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.8k次。点云配准主要针对点云的:不完整、旋转错位、平移错位。因此要得到完整点云就需要对局部点云进行配准。为了得到被测物体的完整数据模型,需要确定一个合适的坐标系变换,将从各个视角得到的点集合并到一个统一的坐标系下形成一个完整的数据点云,然后就可以方便地进行可视化,这就是点云数据的配准。点云配准技术通过计算机技术和统计学规律,通过计算机计算两个点云之间的错位,也就是把在不同的坐标系下的得到的点云进行坐标变..._局部点云与全局点云配准
python零基础学习书-Python零基础到进阶必读的书藉:Python学习手册pdf免费下载-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读273次。提取码:0oorGoogle和YouTube由于Python的高可适应性、易于维护以及适合于快速开发而采用它。如果你想要编写高质量、高效的并且易于与其他语言和工具集成的代码,《Python学习手册:第4 版》将帮助你使用Python快速实现这一点,不管你是编程新手还是Python初学者。本书是易于掌握和自学的教程,根据作者Python专家Mark Lutz的著名培训课程编写而成。《Python学习..._零基础学pythonpdf电子书