cartographer+navigation定位及里程计调试实验记录(一)_cartographer+nav1-程序员宅基地
技术标签: 室内机器人专栏
实验时间: 2021.08.17-2021.08.21
实验地点: 科技园B座一楼楼道
调试内容:
1、0.2m/s速度重新建图的定位效果;
2、cartographer重定位的时间;
3、手动设置初始点实现重定位。
实验重要部分记录:
(1)建图的时候,用以下方法较好,用offline_XXX需要另外配置参数:
roslaunch cartographer_ros demo_backpack_2d.launch bag_filename:=floor_12.bag
rosservice call /finish_trajectory 0
rosservice call /write_state "{filename: '${
HOME}/Downloads/floor_12.pbstream'}"
rosrun cartographer_ros cartographer_pbstream_to_ros_map -map_filestem=/XXX/floor_12 -pbstream_filename=/XXX/floor_12.pbstream -resolution=0.05
并且要配置lua文件参数,lua文件参数会影响建图效果。
demo_backpack_2d.launch文件内容如下:
<launch>
<param name="/use_sim_time" value="true" />
<include file="$(find cartographer_ros)/launch/backpack_2d.launch" />
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" required="true"
args="-d $(find cartographer_ros)/configuration_files/demo_2d.rviz" />
<node name="playbag" pkg="rosbag" type="play"
args="--clock $(arg bag_filename)" />
</launch>
backpack_2d.launch文件内容:
<launch>
<param name="robot_description"
textfile="$(find cartographer_ros)/urdf/backpack_2d.urdf" />
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher"
type="robot_state_publisher" />
<node name="cartographer_node" pkg="cartographer_ros"
type="cartographer_node" args="
-configuration_directory $(find cartographer_ros)/configuration_files
-configuration_basename backpack_2d.lua"
output="screen">
<remap from="scan" to="scan" />
</node>
<node name="cartographer_occupancy_grid_node" pkg="cartographer_ros"
type="cartographer_occupancy_grid_node" args="-resolution 0.05" />
</launch>
backpack_2d.lua文件内容:
include "map_builder.lua"
include "trajectory_builder.lua"
options = {
map_builder = MAP_BUILDER,
trajectory_builder = TRAJECTORY_BUILDER,
map_frame = "map",
tracking_frame = "base_link",
published_frame = "base_link",
odom_frame = "odom",
provide_odom_frame = true,
publish_frame_projected_to_2d = false,
use_pose_extrapolator = true,
use_odometry = false,
use_nav_sat = false,
use_landmarks = false,
num_laser_scans = 1,
num_multi_echo_laser_scans = 0,
num_subdivisions_per_laser_scan = 1,
num_point_clouds = 0,
lookup_transform_timeout_sec = 0.2,
submap_publish_period_sec = 0.3,
pose_publish_period_sec = 5e-3,
trajectory_publish_period_sec = 30e-3,
rangefinder_sampling_ratio = 1.,
odometry_sampling_ratio = 1.,
fixed_frame_pose_sampling_ratio = 1.,
imu_sampling_ratio = 1.,
landmarks_sampling_ratio = 1.,
}
MAP_BUILDER.use_trajectory_builder_2d = true
TRAJECTORY_BUILDER_2D.num_accumulated_range_data = 4
return options
这里面需要格外注意 published_frame = "base_link", provide_odom_frame = true, use_odometry = false,这三个参数。
一般地,建图最好只用激光的数据(/scan)或者是/scan+/odom+/imu。尽量不要是/scan+/odom。
(2)修图的时候一定不能将原始图尺寸做修改,否则可能初始位置不准。修图只用清除一些杂点,添加禁行线(禁行区)。设置禁行线的时候,尽量贴着地图边界,确保把扫描边界包围进去。
(3)将pbstream、pgm和yaml拷贝到导航包的对应文件夹内,并记下路径。修图的禁行线csv文件也要放在read_markfile_pub文件夹下。最重要的是,新建地图后,还要更新cartographer文件中的定位launch文件,写入对应的pbstream文件路径
否则,机器人定位的时候有可能里程计严重漂移。一开始,定位就失败了,里程计坐标系乱跳。
(4)测试cartographer重定位的时候,在距离初始点45米初,有时候可以成功定位,有时候等待五六分钟也定位不成功。在重定位的时候,或者导航过程中,cartographer可以自动优化地图,更新定位。
(5)设置初始点校正机器人位置,在机器人附近,根据机器人位姿设置初始化点,大概率可以重定位成功。
initial_pose_set.cpp
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "cartographer_ros_msgs/FinishTrajectory.h"
#include "cartographer_ros_msgs/StartTrajectory.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovarianceStamped.h"
#include "tf/tf.h"
ros::Subscriber _pose_init_sub;
int traj_id = 1;
void init_pose_callback(const geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped::ConstPtr &msg)
{
double x = msg->pose.pose.position.x;
double y = msg->pose.pose.position.y;
double theta = tf::getYaw(msg->pose.pose.orientation);
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::ServiceClient client_traj_finish = nh.serviceClient<cartographer_ros_msgs::FinishTrajectory>("finish_trajectory");
cartographer_ros_msgs::FinishTrajectory srv_traj_finish;
srv_traj_finish.request.trajectory_id = traj_id;
if (client_traj_finish.call(srv_traj_finish))
{
ROS_INFO("Call finish_trajectory %d success!", traj_id);
}
else
{
ROS_INFO("Failed to call finish_trajectory service!");
}
ros::ServiceClient client_traj_start = nh.serviceClient<cartographer_ros_msgs::StartTrajectory>("start_trajectory");
cartographer_ros_msgs::StartTrajectory srv_traj_start;
srv_traj_start.request.configuration_directory = "/home/lp_hy/carto_ws/install_isolated/share/cartographer_ros/configuration_files";//.lua文件所在路径
srv_traj_start.request.configuration_basename = "backpack_2d_localization_test.lua";//lua文件
srv_traj_start.request.use_initial_pose = 1;
srv_traj_start.request.initial_pose = msg->pose.pose;
srv_traj_start.request.relative_to_trajectory_id = 0;
printf("&&&&&: %f__%f\n",srv_traj_start.request.initial_pose.position.x,srv_traj_start.request.initial_pose.position.y);
if (client_traj_start.call(srv_traj_start))
{
// ROS_INFO("Status ", srv_traj_finish.response.status)
ROS_INFO("Call start_trajectory %d success!", traj_id);
traj_id++;
}
else
{
ROS_INFO("Failed to call start_trajectory service!");
}
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc,argv,"initial_pose_set");
ros::NodeHandle n;
_pose_init_sub = n.subscribe("/initialpose", 1000, &init_pose_callback);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(initial_pose_set)
## Compile as C++11, supported in ROS Kinetic and newer
# add_compile_options(-std=c++11)
## Find catkin macros and libraries
## if COMPONENTS list like find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS xyz)
## is used, also find other catkin packages
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
geometry_msgs
roscpp
cartographer_ros_msgs
tf
)
## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
# find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)
## Uncomment this if the package has a setup.py. This macro ensures
## modules and global scripts declared therein get installed
## See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/user_guide/setup_dot_py.html
# catkin_python_setup()
################################################
## Declare ROS messages, services and actions ##
################################################
## To declare and build messages, services or actions from within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * Let MSG_DEP_SET be the set of packages whose message types you use in
## your messages/services/actions (e.g. std_msgs, actionlib_msgs, ...).
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend tag for "message_generation"
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for each package in MSG_DEP_SET
## * If MSG_DEP_SET isn't empty the following dependency has been pulled in
## but can be declared for certainty nonetheless:
## * add a exec_depend tag for "message_runtime"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "message_generation" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * add "message_runtime" and every package in MSG_DEP_SET to
## catkin_package(CATKIN_DEPENDS ...)
## * uncomment the add_*_files sections below as needed
## and list every .msg/.srv/.action file to be processed
## * uncomment the generate_messages entry below
## * add every package in MSG_DEP_SET to generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES ...)
## Generate messages in the 'msg' folder
# add_message_files(
# FILES
# Message1.msg
# Message2.msg
# )
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder
# add_service_files(
# FILES
# Service1.srv
# Service2.srv
# )
## Generate actions in the 'action' folder
# add_action_files(
# FILES
# Action1.action
# Action2.action
# )
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here
# generate_messages(
# DEPENDENCIES
# geometry_msgs
# )
################################################
## Declare ROS dynamic reconfigure parameters ##
################################################
## To declare and build dynamic reconfigure parameters within this
## package, follow these steps:
## * In the file package.xml:
## * add a build_depend and a exec_depend tag for "dynamic_reconfigure"
## * In this file (CMakeLists.txt):
## * add "dynamic_reconfigure" to
## find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS ...)
## * uncomment the "generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options" section below
## and list every .cfg file to be processed
## Generate dynamic reconfigure parameters in the 'cfg' folder
# generate_dynamic_reconfigure_options(
# cfg/DynReconf1.cfg
# cfg/DynReconf2.cfg
# )
###################################
## catkin specific configuration ##
###################################
## The catkin_package macro generates cmake config files for your package
## Declare things to be passed to dependent projects
## INCLUDE_DIRS: uncomment this if your package contains header files
## LIBRARIES: libraries you create in this project that dependent projects also need
## CATKIN_DEPENDS: catkin_packages dependent projects also need
## DEPENDS: system dependencies of this project that dependent projects also need
catkin_package(
# INCLUDE_DIRS include
# LIBRARIES initial_pose_set
CATKIN_DEPENDS geometry_msgs roscpp cartographer_ros_msgs tf
# DEPENDS system_lib
)
###########
## Build ##
###########
## Specify additional locations of header files
## Your package locations should be listed before other locations
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
## Declare a C++ library
# add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
# src/${PROJECT_NAME}/initial_pose_set.cpp
# )
## Add cmake target dependencies of the library
## as an example, code may need to be generated before libraries
## either from message generation or dynamic reconfigure
# add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Declare a C++ executable
## With catkin_make all packages are built within a single CMake context
## The recommended prefix ensures that target names across packages don't collide
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} src/initial_pose_set.cpp)
## Rename C++ executable without prefix
## The above recommended prefix causes long target names, the following renames the
## target back to the shorter version for ease of user use
## e.g. "rosrun someones_pkg node" instead of "rosrun someones_pkg someones_pkg_node"
# set_target_properties(${PROJECT_NAME}_node PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME node PREFIX "")
## Add cmake target dependencies of the executable
## same as for the library above
add_dependencies(${PROJECT_NAME} ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
## Specify libraries to link a library or executable target against
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
)
#############
## Install ##
#############
# all install targets should use catkin DESTINATION variables
# See http://ros.org/doc/api/catkin/html/adv_user_guide/variables.html
## Mark executable scripts (Python etc.) for installation
## in contrast to setup.py, you can choose the destination
# catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS
# scripts/my_python_script
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark executables for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_executables.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}_node
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark libraries for installation
## See http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/catkin/html/howto/format1/building_libraries.html
# install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}
# ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_LIB_DESTINATION}
# RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CATKIN_GLOBAL_BIN_DESTINATION}
# )
## Mark cpp header files for installation
# install(DIRECTORY include/${PROJECT_NAME}/
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_INCLUDE_DESTINATION}
# FILES_MATCHING PATTERN "*.h"
# PATTERN ".svn" EXCLUDE
# )
## Mark other files for installation (e.g. launch and bag files, etc.)
# install(FILES
# # myfile1
# # myfile2
# DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}
# )
#############
## Testing ##
#############
## Add gtest based cpp test target and link libraries
# catkin_add_gtest(${PROJECT_NAME}-test test/test_initial_pose_set.cpp)
# if(TARGET ${PROJECT_NAME}-test)
# target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}-test ${PROJECT_NAME})
# endif()
## Add folders to be run by python nosetests
# catkin_add_nosetests(test)
(6)怎样验证里程计数据精度?
机器人掉电重启,确保/odom坐标原点与/map原点一致(0,0)。
启动机器人节点,然后发布速度
rostopic pub -r 10 /cmd_vel “Tab补全”
另开终端运行
rostopic echo /odom
让机器人前进一段距离,然后对比分析positon:x和y(横向距离和纵向距离误差)
实际值用尺子测量,与里程计/odom的值对比。例如:
初始点(0,0,0),以0.1m/s速度前进8米;
结果,机器人x轴实际值8米,里程计值8.01米;y轴实际值0.2米,里程计值0.005米。
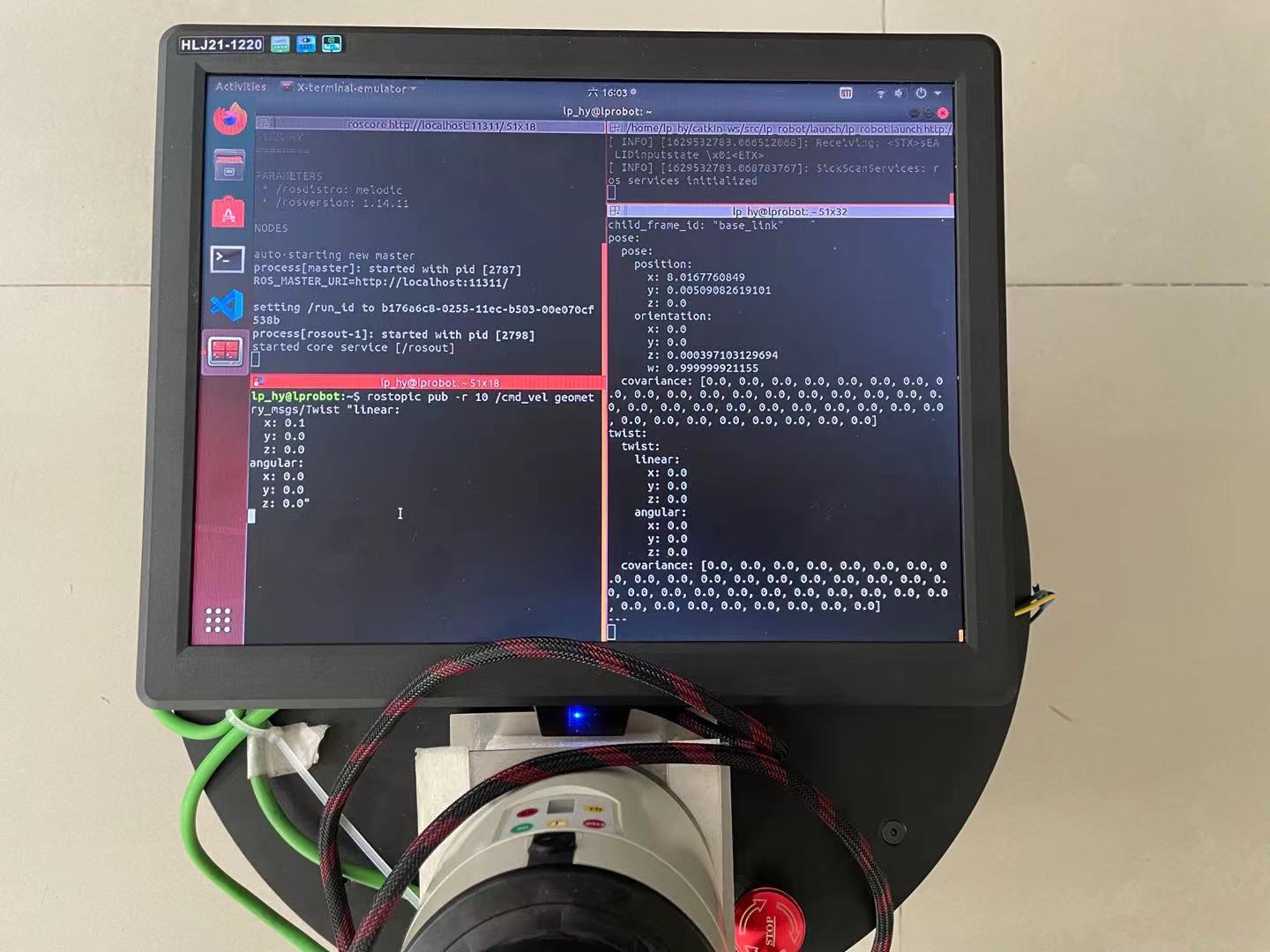
结论:里程计数据精度基本可以,做SLAM定位导航问题不大。
智能推荐
攻防世界_难度8_happy_puzzle_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读645次。这个肯定是末尾的IDAT了,因为IDAT必须要满了才会开始一下个IDAT,这个明显就是末尾的IDAT了。,对应下面的create_head()代码。,对应下面的create_tail()代码。不要考虑爆破,我已经试了一下,太多情况了。题目来源:UNCTF。_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文
达梦数据库的导出(备份)、导入_达梦数据库导入导出-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次,点赞3次,收藏10次。偶尔会用到,记录、分享。1. 数据库导出1.1 切换到dmdba用户su - dmdba1.2 进入达梦数据库安装路径的bin目录,执行导库操作 导出语句:./dexp cwy_init/[email protected]:5236 file=cwy_init.dmp log=cwy_init_exp.log 注释: cwy_init/init_123..._达梦数据库导入导出
js引入kindeditor富文本编辑器的使用_kindeditor.js-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.9k次。1. 在官网上下载KindEditor文件,可以删掉不需要要到的jsp,asp,asp.net和php文件夹。接着把文件夹放到项目文件目录下。2. 修改html文件,在页面引入js文件:<script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/kindeditor-all.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/lang/zh-CN.js"_kindeditor.js
STM32学习过程记录11——基于STM32G431CBU6硬件SPI+DMA的高效WS2812B控制方法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次,点赞6次,收藏14次。SPI的详情简介不必赘述。假设我们通过SPI发送0xAA,我们的数据线就会变为10101010,通过修改不同的内容,即可修改SPI中0和1的持续时间。比如0xF0即为前半周期为高电平,后半周期为低电平的状态。在SPI的通信模式中,CPHA配置会影响该实验,下图展示了不同采样位置的SPI时序图[1]。CPOL = 0,CPHA = 1:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在下降沿采样,并在上升沿移出CPOL = 0,CPHA = 0:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在上升沿采样,并在下降沿移出。_stm32g431cbu6
计算机网络-数据链路层_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次,点赞2次,收藏8次。数据链路层习题自测问题1.数据链路(即逻辑链路)与链路(即物理链路)有何区别?“电路接通了”与”数据链路接通了”的区别何在?2.数据链路层中的链路控制包括哪些功能?试讨论数据链路层做成可靠的链路层有哪些优点和缺点。3.网络适配器的作用是什么?网络适配器工作在哪一层?4.数据链路层的三个基本问题(帧定界、透明传输和差错检测)为什么都必须加以解决?5.如果在数据链路层不进行帧定界,会发生什么问题?6.PPP协议的主要特点是什么?为什么PPP不使用帧的编号?PPP适用于什么情况?为什么PPP协议不_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输
软件测试工程师移民加拿大_无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读587次。软件测试工程师移民加拿大 无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分) (Undocumented Immigrant With No Education to Software Engineer(Part 1))Before I start, I want you to please bear with me on the way I write, I have very little gen...
随便推点
Thinkpad X250 secure boot failed 启动失败问题解决_安装完系统提示secureboot failure-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读304次。Thinkpad X250笔记本电脑,装的是FreeBSD,进入BIOS修改虚拟化配置(其后可能是误设置了安全开机),保存退出后系统无法启动,显示:secure boot failed ,把自己惊出一身冷汗,因为这台笔记本刚好还没开始做备份.....根据错误提示,到bios里面去找相关配置,在Security里面找到了Secure Boot选项,发现果然被设置为Enabled,将其修改为Disabled ,再开机,终于正常启动了。_安装完系统提示secureboot failure
C++如何做字符串分割(5种方法)_c++ 字符串分割-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读10w+次,点赞93次,收藏352次。1、用strtok函数进行字符串分割原型: char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);功能:分解字符串为一组字符串。参数说明:str为要分解的字符串,delim为分隔符字符串。返回值:从str开头开始的一个个被分割的串。当没有被分割的串时则返回NULL。其它:strtok函数线程不安全,可以使用strtok_r替代。示例://借助strtok实现split#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h&_c++ 字符串分割
2013第四届蓝桥杯 C/C++本科A组 真题答案解析_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次。1 .高斯日记 大数学家高斯有个好习惯:无论如何都要记日记。他的日记有个与众不同的地方,他从不注明年月日,而是用一个整数代替,比如:4210后来人们知道,那个整数就是日期,它表示那一天是高斯出生后的第几天。这或许也是个好习惯,它时时刻刻提醒着主人:日子又过去一天,还有多少时光可以用于浪费呢?高斯出生于:1777年4月30日。在高斯发现的一个重要定理的日记_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答
基于供需算法优化的核极限学习机(KELM)分类算法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读851次,点赞17次,收藏22次。摘要:本文利用供需算法对核极限学习机(KELM)进行优化,并用于分类。
metasploitable2渗透测试_metasploitable2怎么进入-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1k次。一、系统弱密码登录1、在kali上执行命令行telnet 192.168.26.1292、Login和password都输入msfadmin3、登录成功,进入系统4、测试如下:二、MySQL弱密码登录:1、在kali上执行mysql –h 192.168.26.129 –u root2、登录成功,进入MySQL系统3、测试效果:三、PostgreSQL弱密码登录1、在Kali上执行psql -h 192.168.26.129 –U post..._metasploitable2怎么进入
Python学习之路:从入门到精通的指南_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读257次。本文将为初学者提供Python学习的详细指南,从Python的历史、基础语法和数据类型到面向对象编程、模块和库的使用。通过本文,您将能够掌握Python编程的核心概念,为今后的编程学习和实践打下坚实基础。_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf