【Python知识】可视化函数plt.scatter-程序员宅基地
技术标签: python 机器学习 python指南和应用 numpy
目录
一、说明
关于matplotlib的scatter函数有许多活动参数,如果不专门注解,是无法掌握精髓的,本文专门针对scatter的参数和调用说起,并配有若干案例。
二、函数和参数详解
2.1 scatter函数原型
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, *, edgecolors=None, plotnonfinite=False, data=None, **kwargs)
2.2 参数详解
| 属性 | 参数 | 意义 |
| 坐标 | x,y | 输入点列的数组,长度都是size |
| 点大小 | s | 点的直径数组,默认直径20,长度最大size |
| 点颜色 | c | 点的颜色,默认蓝色 'b',也可以是个 RGB 或 RGBA 二维行数组。 |
| 点形状 | marker | 点的样式,默认小圆圈 'o'。 |
| 调色板 | cmap | Colormap,默认 None,标量或者是一个 colormap 的名字,只有 c 是一个浮点数数组时才使用。如果没有申明就是 image.cmap。 |
| 亮度(1) | norm | Normalize,默认 None,数据亮度在 0-1 之间,只有 c 是一个浮点数的数组的时才使用。 |
| 亮度(2) | vmin,vmax | 亮度设置,在 norm 参数存在时会忽略。 |
| 透明度 | alpha | 透明度设置,0-1 之间,默认 None,即不透明 |
| 线 | linewidths | 标记点的长度 |
| 颜色 | edgecolors |
颜色或颜色序列,默认为 'face',可选值有 'face', 'none', None。 |
| plotnonfinite |
布尔值,设置是否使用非限定的 c ( inf, -inf 或 nan) 绘制点。 | |
| **kwargs |
其他参数。 |
2.3 其中散点的形状参数marker如下:


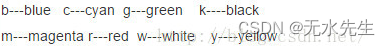
2.4 其中颜色参数c如下:
三、画图示例
3.1 关于坐标x,y和s,c
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
N = 50
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
colors = np.random.rand(N) # 颜色可以随机
area = (30 * np.random.rand(N))**2 # 点的宽度30,半径15
plt.scatter(x, y, s=area, c=colors, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
注意:以上核心语句是:
plt.scatter(x, y, s=area, c=colors, alpha=0.5, marker=",")
其中:x,y,s,c维度一样就能成。
3.2 多元高斯的情况
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
#Generating a Gaussion dataset:
#creating random vectors from the multivariate normal distribution
#given mean and covariance
mu_vec1=np.array([0,0])
cov_mat1=np.array([[1,0],[0,1]])
X=np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vec1,cov_mat1,500)
R=X**2
R_sum=R.sum(axis=1)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],color='green',marker='o', =32.*R_sum,edgecolor='black',alpha=0.5)
plt.show()

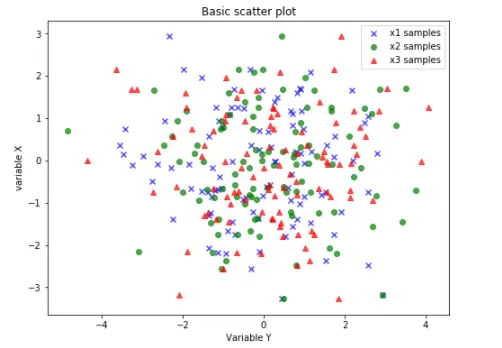
3.3 绘制例子
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Generating a Gaussion dTset:
#Creating random vectors from the multivaritate normal distribution
#givem mean and covariance
mu_vecl = np.array([0, 0])
cov_matl = np.array([[2,0],[0,2]])
x1_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vecl, cov_matl,100)
x2_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vecl+0.2, cov_matl +0.2, 100)
x3_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vecl+0.4, cov_matl +0.4, 100)
plt.figure(figsize = (8, 6))
plt.scatter(x1_samples[:,0], x1_samples[:, 1], marker='x',
color = 'blue', alpha=0.7, label = 'x1 samples')
plt.scatter(x2_samples[:,0], x1_samples[:,1], marker='o',
color ='green', alpha=0.7, label = 'x2 samples')
plt.scatter(x3_samples[:,0], x1_samples[:,1], marker='^',
color ='red', alpha=0.7, label = 'x3 samples')
plt.title('Basic scatter plot')
plt.ylabel('variable X')
plt.xlabel('Variable Y')
plt.legend(loc = 'upper right')
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([0],[0], marker="o", markersize=10)
ax.plot([0.07,0.93],[0,0], linewidth=10)
ax.scatter([1],[0], s=100)
ax.plot([0],[1], marker="o", markersize=22)
ax.plot([0.14,0.86],[1,1], linewidth=22)
ax.scatter([1],[1], s=22**2)
plt.show()

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
for dpi in [72,100,144]:
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.5,2), dpi=dpi)
ax.set_title("fig.dpi={}".format(dpi))
ax.set_ylim(-3,3)
ax.set_xlim(-2,2)
ax.scatter([0],[1], s=10**2,
marker="s", linewidth=0, label="100 points^2")
ax.scatter([1],[1], s=(10*72./fig.dpi)**2,
marker="s", linewidth=0, label="100 pixels^2")
ax.legend(loc=8,framealpha=1, fontsize=8)
fig.savefig("fig{}.png".format(dpi), bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()
3.4 绘图例3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
for dpi in [72,100,144]:
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.5,2), dpi=dpi)
ax.set_title("fig.dpi={}".format(dpi))
ax.set_ylim(-3,3)
ax.set_xlim(-2,2)
ax.scatter([0],[1], s=10**2,
marker="s", linewidth=0, label="100 points^2")
ax.scatter([1],[1], s=(10*72./fig.dpi)**2,
marker="s", linewidth=0, label="100 pixels^2")
ax.legend(loc=8,framealpha=1, fontsize=8)
fig.savefig("fig{}.png".format(dpi), bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()

3.5 同心绘制
plt.scatter(2, 1, s=4000, c='r')
plt.scatter(2, 1, s=1000 ,c='b')
plt.scatter(2, 1, s=10, c='g')

3.6 有标签绘制
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_coords = [0.13, 0.22, 0.39, 0.59, 0.68, 0.74,0.93]
y_coords = [0.75, 0.34, 0.44, 0.52, 0.80, 0.25,0.55]
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (8,5))
plt.scatter(x_coords, y_coords, marker = 's', s = 50)
for x, y in zip(x_coords, y_coords):
plt.annotate('(%s,%s)'%(x,y), xy=(x,y),xytext = (0, -10), textcoords = 'offset points',ha = 'center', va = 'top')
plt.xlim([0,1])
plt.ylim([0,1])
plt.show()

3.7 直线划分
# 2-category classfication with random 2D-sample data
# from a multivariate normal distribution
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def decision_boundary(x_1):
"""Calculates the x_2 value for plotting the decision boundary."""
# return 4 - np.sqrt(-x_1**2 + 4*x_1 + 6 + np.log(16))
return -x_1 + 1
# Generating a gaussion dataset:
# creating random vectors from the multivariate normal distribution
# given mean and covariance
mu_vec1 = np.array([0,0])
cov_mat1 = np.array([[2,0],[0,2]])
x1_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vec1, cov_mat1,100)
mu_vec1 = mu_vec1.reshape(1,2).T # TO 1-COL VECTOR
mu_vec2 = np.array([1,2])
cov_mat2 = np.array([[1,0],[0,1]])
x2_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vec2, cov_mat2, 100)
mu_vec2 = mu_vec2.reshape(1,2).T # to 2-col vector
# Main scatter plot and plot annotation
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7, 7))
ax.scatter(x1_samples[:, 0], x1_samples[:,1], marker = 'o',color = 'green', s=40)
ax.scatter(x2_samples[:, 0], x2_samples[:,1], marker = '^',color = 'blue', s =40)
plt.legend(['Class1 (w1)', 'Class2 (w2)'], loc = 'upper right')
plt.title('Densities of 2 classes with 25 bivariate random patterns each')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.xlabel('x1')
ftext = 'p(x|w1) -N(mu1=(0,0)^t, cov1 = I)\np.(x|w2) -N(mu2 = (1, 1)^t), cov2 =I'
plt.figtext(.15,.8, ftext, fontsize = 11, ha ='left')
#Adding decision boundary to plot
x_1 = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
bound = decision_boundary(x_1)
plt.plot(x_1, bound, 'r--', lw = 3)
x_vec = np.linspace(*ax.get_xlim())
x_1 = np.arange(0, 100, 0.05)
plt.show()

3.8 曲线划分
# 2-category classfication with random 2D-sample data
# from a multivariate normal distribution
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def decision_boundary(x_1):
"""Calculates the x_2 value for plotting the decision boundary."""
return 4 - np.sqrt(-x_1**2 + 4*x_1 + 6 + np.log(16))
# Generating a gaussion dataset:
# creating random vectors from the multivariate normal distribution
# given mean and covariance
mu_vec1 = np.array([0,0])
cov_mat1 = np.array([[2,0],[0,2]])
x1_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vec1, cov_mat1,100)
mu_vec1 = mu_vec1.reshape(1,2).T # TO 1-COL VECTOR
mu_vec2 = np.array([1,2])
cov_mat2 = np.array([[1,0],[0,1]])
x2_samples = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu_vec2, cov_mat2, 100)
mu_vec2 = mu_vec2.reshape(1,2).T # to 2-col vector
# Main scatter plot and plot annotation
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7, 7))
ax.scatter(x1_samples[:, 0], x1_samples[:,1], marker = 'o',color = 'green', s=40)
ax.scatter(x2_samples[:, 0], x2_samples[:,1], marker = '^',color = 'blue', s =40)
plt.legend(['Class1 (w1)', 'Class2 (w2)'], loc = 'upper right')
plt.title('Densities of 2 classes with 25 bivariate random patterns each')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.xlabel('x1')
ftext = 'p(x|w1) -N(mu1=(0,0)^t, cov1 = I)\np.(x|w2) -N(mu2 = (1, 1)^t), cov2 =I'
plt.figtext(.15,.8, ftext, fontsize = 11, ha ='left')
#Adding decision boundary to plot
x_1 = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
bound = decision_boundary(x_1)
plt.plot(x_1, bound, 'r--', lw = 3)
x_vec = np.linspace(*ax.get_xlim())
x_1 = np.arange(0, 100, 0.05)
plt.show()

智能推荐
js-选项卡原理_选项卡js原理-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读90次。【代码】js-选项卡原理。_选项卡js原理
设计模式-原型模式(Prototype)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读67次。原型模式是一种对象创建型模式,它采用复制原型对象的方法来创建对象的实例。它创建的实例,具有与原型一样的数据结构和值分为深度克隆和浅度克隆。浅度克隆:克隆对象的值类型(基本数据类型),克隆引用类型的地址;深度克隆:克隆对象的值类型,引用类型的对象也复制一份副本。UML图:具体代码:浅度复制:import java.util.List;/*..._prototype 设计模式
个性化政府云的探索-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读59次。入选国内首批云计算服务创新发展试点城市的北京、上海、深圳、杭州和无锡起到了很好的示范作用,不仅促进了当地产业的升级换代,而且为国内其他城市发展云计算产业提供了很好的借鉴。据了解,目前国内至少有20个城市确定将云计算作为重点发展的产业。这势必会形成新一轮的云计算基础设施建设的**。由于云计算基础设施建设具有投资规模大,运维成本高,投资回收周期长,地域辐射性强等诸多特点,各地在建...
STM32问题集之BOOT0和BOOT1的作用_stm32boot0和boot1作用-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读9.4k次,点赞2次,收藏20次。一、功能及目的 在每个STM32的芯片上都有两个管脚BOOT0和BOOT1,这两个管脚在芯片复位时的电平状态决定了芯片复位后从哪个区域开始执行程序。BOOT1=x BOOT0=0 // 从用户闪存启动,这是正常的工作模式。BOOT1=0 BOOT0=1 // 从系统存储器启动,这种模式启动的程序_stm32boot0和boot1作用
C语言函数递归调用-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.4k次,点赞2次,收藏22次。C语言函数递归调用_c语言函数递归调用
明日方舟抽卡模拟器wiki_明日方舟bilibili服-明日方舟bilibili服下载-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读410次。明日方舟bilibili服是一款天灾驾到战斗热血的创新二次元废土风塔防手游,精妙的二次元纸片人设计,为宅友们源源不断更新超多的纸片人老婆老公们,玩家将扮演废土正义一方“罗德岛”中的指挥官,与你身边的感染者们并肩作战。与同类塔防手游与众不同的几点,首先你可以在这抽卡轻松获得稀有,同时也可以在战斗体系和敌军走位机制看到不同。明日方舟bilibili服设定:1、起因不明并四处肆虐的天灾,席卷过的土地上出..._明日方舟抽卡模拟器
随便推点
Maven上传Jar到私服报错:ReasonPhrase: Repository version policy: SNAPSHOT does not allow version: xxx_repository version policy snapshot does not all-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读437次。Maven上传Jar到私服报错:ReasonPhrase: Repository version policy: SNAPSHOT does not allow version: xxx_repository version policy snapshot does not all
斐波那契数列、素数、质数和猴子吃桃问题_斐波那契日-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次。斐波那契数列(Fibonacci Sequence)是由如下形式的一系列数字组成的:0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …上述数字序列中反映出来的规律,就是下一个数字是该数字前面两个紧邻数字的和,具体如下所示:示例:比如上述斐波那契数列中的最后两个数,可以推导出34后面的数为21+34=55下面是一个更长一些的斐波那契数列:0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584,_斐波那契日
PHP必会面试题_//该层循环用来控制每轮 冒出一个数 需要比较的次数-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读363次。PHP必会面试题1. 基础篇1. 用 PHP 打印出前一天的时间格式是 2017-12-28 22:21:21? //>>1.当前时间减去一天的时间,然后再格式化echo date('Y-m-d H:i:s',time()-3600*24);//>>2.使用strtotime,可以将任何字符串时间转换成时间戳,仅针对英文echo date('Y-m-d H:i:s',str..._//该层循环用来控制每轮 冒出一个数 需要比较的次数
windows用mingw(g++)编译opencv,opencv_contrib,并install安装_opencv mingw contrib-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.3k次,点赞26次,收藏26次。windows下用mingw编译opencv貌似不支持cuda,选cuda会报错,我无法解决,所以没选cuda,下面两种编译方式支持。打开cmake gui程序,在下面两个框中分别输入opencv的源文件和编译目录,build-mingw为你创建的目录,可自定义命名。1、如果已经安装Qt,则Qt自带mingw编译器,从Qt安装目录找到编译器所在目录即可。1、如果已经安装Qt,则Qt自带cmake,从Qt安装目录找到cmake所在目录即可。2、若未安装Qt,则安装Mingw即可,参考我的另外一篇文章。_opencv mingw contrib
5个高质量简历模板网站,免费、免费、免费_hoso模板官网-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读10w+次,点赞42次,收藏309次。今天给大家推荐5个好用且免费的简历模板网站,简洁美观,非常值得收藏!1、菜鸟图库https://www.sucai999.com/search/word/0_242_0.html?v=NTYxMjky网站主要以设计类素材为主,办公类素材也很多,简历模板大部个偏简约风,各种版式都有,而且经常会更新。最重要的是全部都能免费下载。2、个人简历网https://www.gerenjianli.com/moban/这是一个专门提供简历模板的网站,里面有超多模板个类,找起来非常方便,风格也很多样,无须注册就能免费下载,_hoso模板官网
通过 TikTok 联盟提高销售额的 6 个步骤_tiktok联盟-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读142次。你听说过吗?该计划可让您以推广您的产品并在成功销售时支付佣金。它提供了新的营销渠道,使您的产品呈现在更广泛的受众面前并提高品牌知名度。此外,TikTok Shop联盟可以是一种经济高效的产品或服务营销方式。您只需在有人购买时付费,因此不存在在无效广告上浪费金钱的风险。这些诱人的好处是否足以让您想要开始您的TikTok Shop联盟活动?如果是这样,本指南适合您。_tiktok联盟